Protocol to detect nucleotide-protein interaction in vitro using a non-radioactive competitive electrophoretic mobility shift assay - ScienceDirect
Par un écrivain mystérieux
Description

Regulatory guidelines and preclinical tools to study the biodistribution of RNA therapeutics - ScienceDirect

Detection of RNA‐protein interactions using a highly sensitive non‐radioactive electrophoretic mobility shift assay - Daras - 2019 - ELECTROPHORESIS - Wiley Online Library

Protocol to detect nucleotide-protein interaction in vitro using a non-radioactive competitive electrophoretic mobility shift assay - ScienceDirect

RNA inhibits dMi-2/CHD4 chromatin binding and nucleosome remodeling - ScienceDirect

Zic5 stabilizes Gli3 via a non-transcriptional mechanism during retinal development - ScienceDirect

PDF) Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay: Analyzing Protein - Nucleic Acid Interactions

Interaction of RSC Chromatin Remodeling Complex with Nucleosomes Is Modulated by H3 K14 Acetylation and H2B SUMOylation In Vivo - ScienceDirect

PDF) Protocol to detect nucleotide-protein interaction in vitro using a non-radioactive competitive electrophoretic mobility shift assay

Mapping chromosomal proteins in vivo by formaldehyde-crosslinked-chromatin immunoprecipitation: Trends in Biochemical Sciences

CTCF DNA-binding domain undergoes dynamic and selective protein–protein interactions - ScienceDirect

Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assays for the Analysis of DNA-Protein Interactions

Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli senses microbiota-derived nicotinamide to increase its virulence and colonization in the large intestine - ScienceDirect

THOC5 complexes with DDX5, DDX17, and CDK12 to regulate R loop structures and transcription elongation rate - ScienceDirect
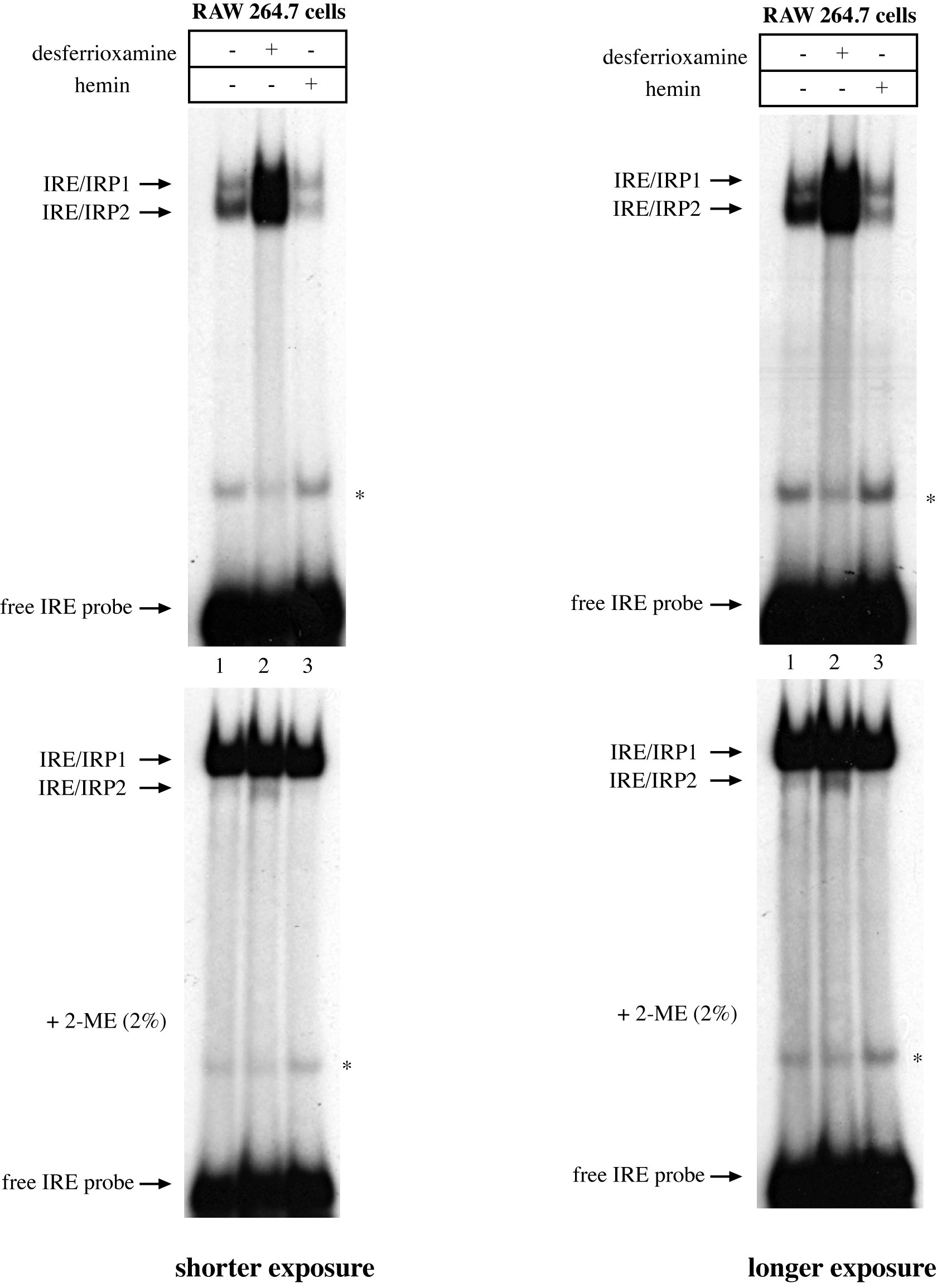
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) for the Study of RNA-Protein Interactions: The IRE/IRP Example

Bacterial H-NS contacts DNA at the same irregularly spaced sites in both bridged and hemi-sequestered linear filaments - ScienceDirect
depuis
par adulte (le prix varie selon la taille du groupe)







