L-Carnitine ((R)-Carnitine), Co-factor for β-oxidation
Par un écrivain mystérieux
Description
L-Carnitine ((R)-Carnitine), a highly polar, small zwitterion, is an essential co-factor for the mitochondrial β-oxidation pathway. L-Carnitine functions to transport long chain fatty acyl-CoAs into the mitochondria for degradation by β-oxidation. L-Carnitine is an antioxidant. L-Carnitine can ameliorate metabolic imbalances in many inborn errors of metabolism. - Mechanism of Action & Protocol.

L-Carnitine

Propionyl l-Carnitine Improvement of Hypertrophied Heart Function Is Accompanied by an Increase in Carbohydrate Oxidation
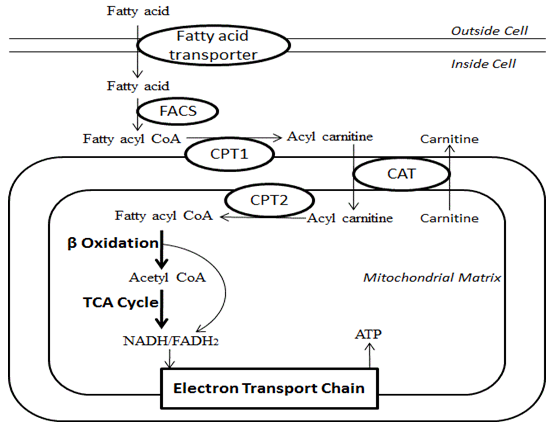
Fatty Acid beta-Oxidation

Carnitine Complex – Naturally Nourished

Targeting Skeletal Muscle Dysfunction With L-Carnitine for the Treatment of Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease

Carnitine Complex – Naturally Nourished
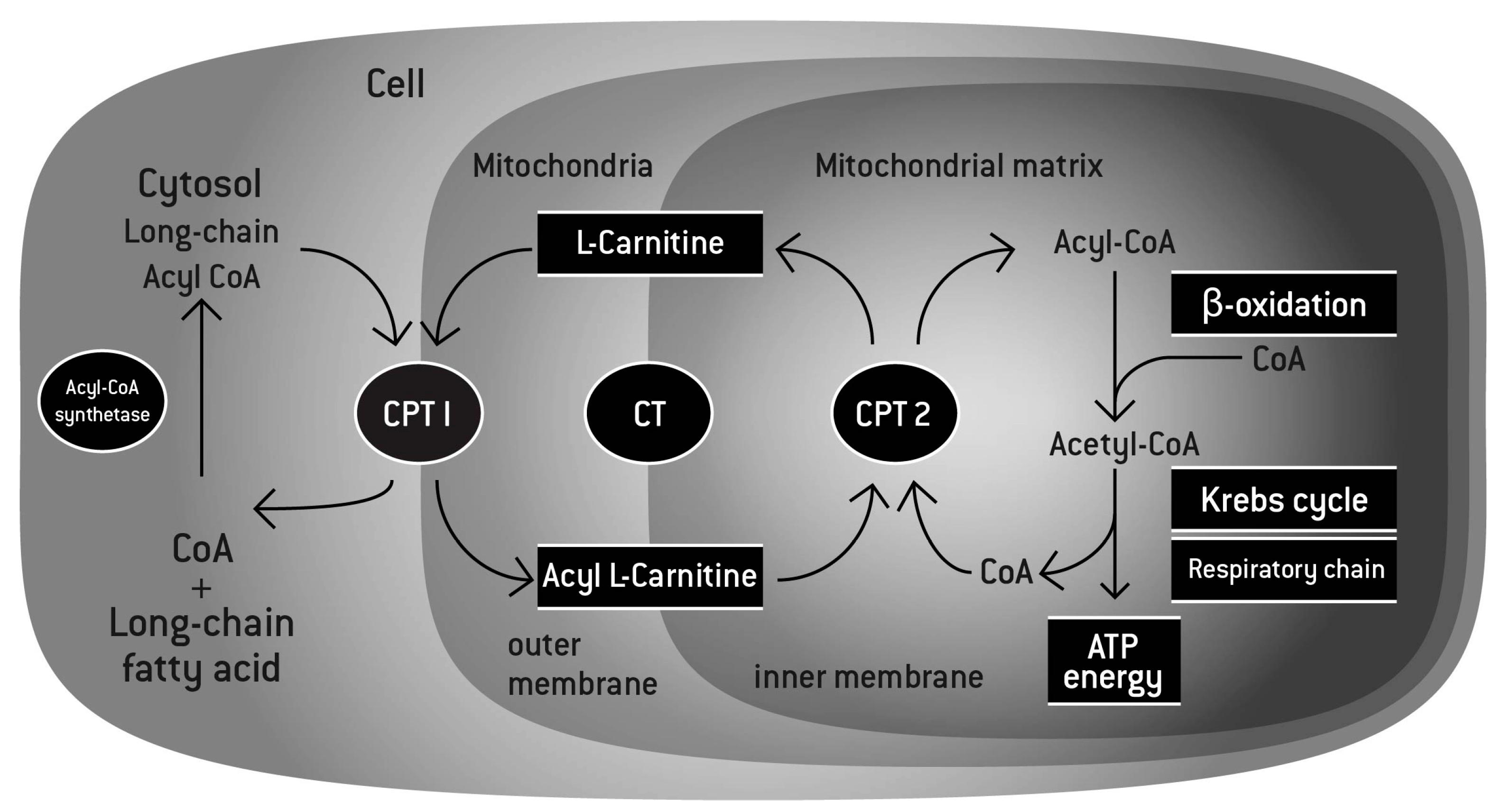
Nutrients, Free Full-Text

Environmental Enteric Dysfunction is Associated with Carnitine Deficiency and Altered Fatty Acid Oxidation - eBioMedicine

Acylcarnitines: Nomenclature, Biomarkers, Therapeutic Potential, Drug Targets, and Clinical Trials
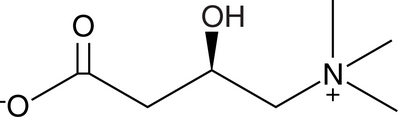
L-Carnitine ((–)-Carnitine, Levocarnitine, R-Carnitine, CAS Number: 541-15-1)
depuis
par adulte (le prix varie selon la taille du groupe)